A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. A WBS is the cornerstone of effective project planning, execution, controlling, monitoring, and reporting. All the work contained within the WBS is to be identified, estimated, scheduled, and budgeted.
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is developed to establish a common understanding of project scope. It is a hierarchical description of the work that must be done to complete the deliverables of a project. Each descending level in the WBS represents an increasingly detailed description of the project deliverables.
The first two levels of the WBS (the root node and Level 2) define a set of planned outcomes that collectively and exclusively represent 100% of the project scope. At each subsequent level, the children of a parent node collectively and exclusively represent 100% of the scope of their parent node. Here is a Work Breakdown Structure example:
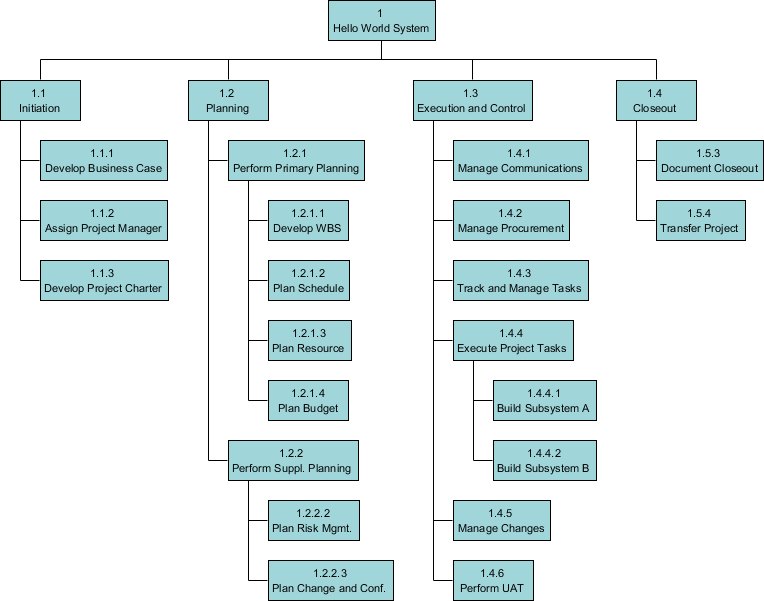
A well-designed WBS describes planned outcomes instead of planned actions. Outcomes are the desired ends of the project, such as a product, result, or service, and can be predicted accurately. Actions, on the other hand, may be difficult to predict accurately. A well-designed WBS makes it easy to assign elements of the WBS to any project activity. A good WBS should exhibit the following characteristics:
The development of Work Breakdown Structure involves subdividing the major project activities or sub-activities into smaller, more manageable activities until the activities are defined in sufficient detail to support the management and development of project works. The items at the lowest level of a branch are known as work packages. Here are some tips in developing a Work Breakdown Structure that can express works effectively:
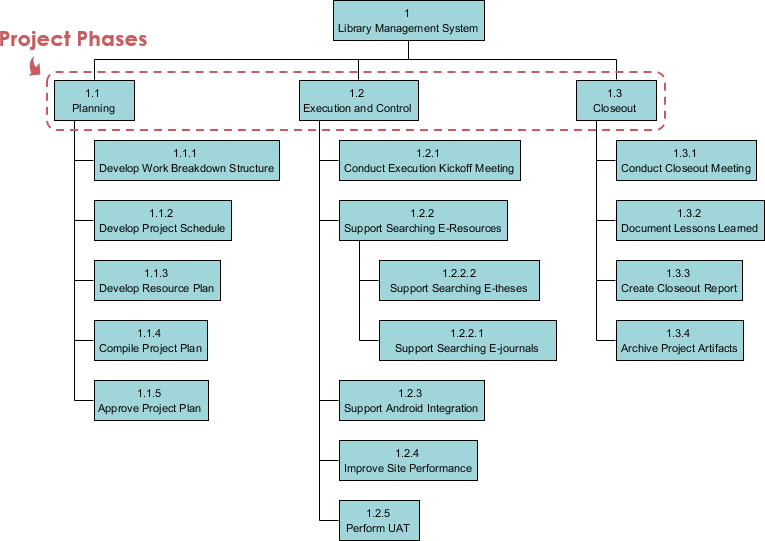
Generally speaking, there are three typical ways in structuring works with a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). They includes phase-based structures, deliverable-based structures and responsibility-based structures.
Define and structure project activities based on the project phases.
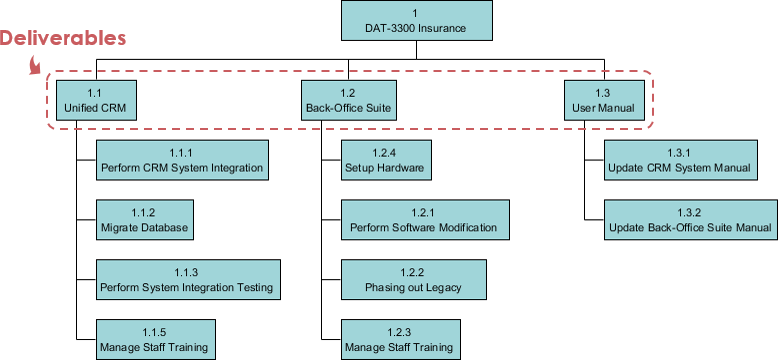
Define and structure project activities based on the deliverables agreed to deliver.
Define and structure project activities based on the organization units that will work on the project.
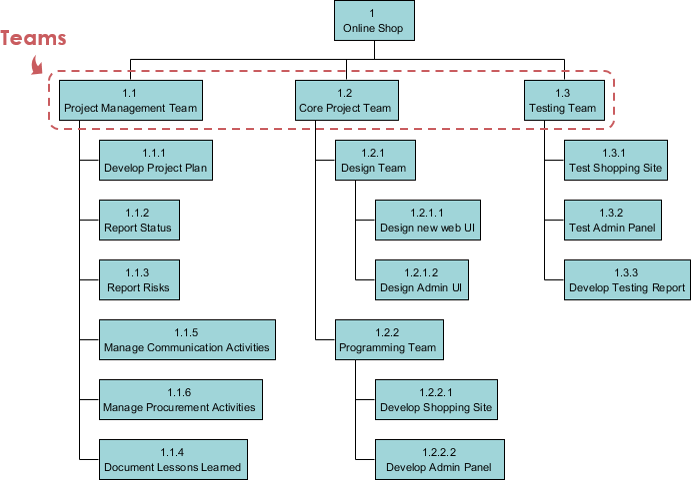
Typical use of breakdown structure as a project management tool includes Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Resource Breakdown Structure, Risk Breakdown Structure and Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS), or sometimes known as Organization Chart.
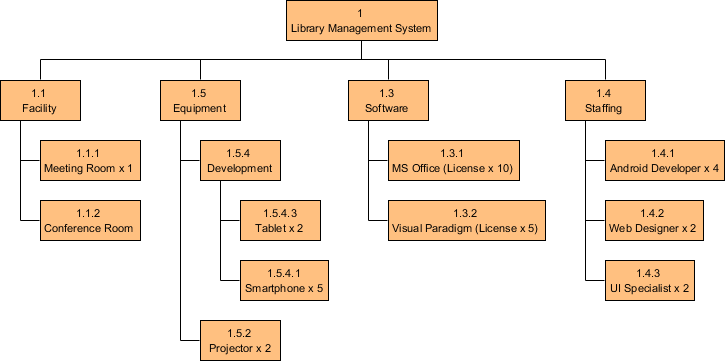
Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a project management tool that provides a hierarchical decomposition of resources, either structured by resource category, types or by IT/business function that has resource needs.
Here is a Resource Breakdown Structure example:
Risks are everything in any IT project. The existence of risk causes negative impact on project schedule, costs and quality. In project management, Project Manager is responsible for managing risks and to ensure that the project will be delivered on time, within project and up to the standard user expected. One of the popular risk management tool is the Risk Breakdown Structure.
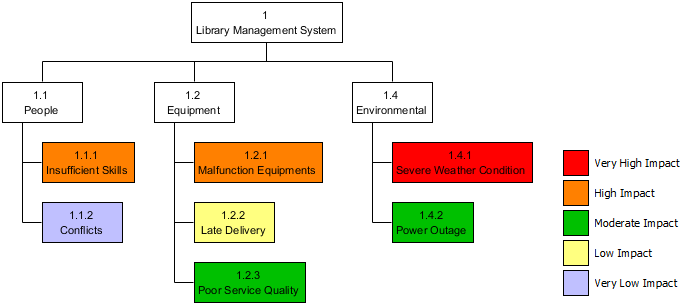
Risk breakdown Structure is the hierarchical decomposition of risks, starting from the root node element that represents the project, and going down to the various risk categories, and then finer level risks.
Besides presenting project risks in a Risk Breakdown Structure, it is possible to combine the use of Color Legend in representing the impact of risk. Take a look at the Risk Breakdown Structure example below, a legend of Impact with five items has been setup, representing the five levels of impacts that risks may have on the project with five distinct color code.
Here is a Risk Breakdown Structure example:
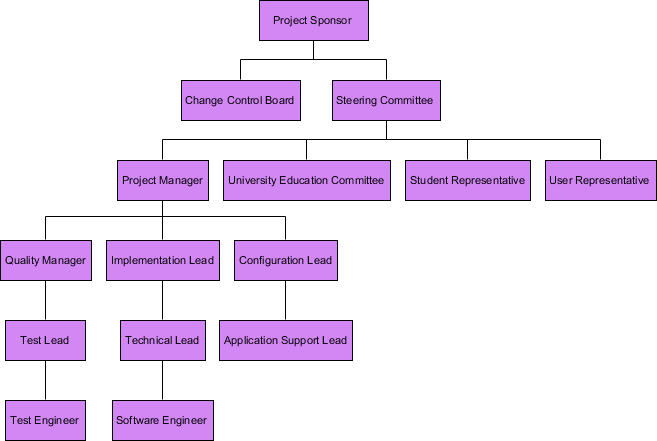
Organizational Breakdown Structure, or sometimes known as Organization Chart, is a widely used project management tool for representing project organization. It typically begins with the project sponsor, and with all key stakeholders included. In presenting the organization structure, consider the organization or group that is requesting the project and the level of their sponsorship and authority.
Here is an Organizational Breakdown Structure example: