Activities are critical components of BPMN - All business processes are primarily formed by different kinds of BPMN activities. With Visual Paradigm, you can draw your own BPMN diagram by using different kinds of activities. In this article, we will explain the different kinds of BPMN 2.0 activities you can use in modeling a business process with BPMN.
Visual Paradigm provides an easy-to-use BPMN tool for you to create BPMN 2.0 diagrams of your own. No matter you want to learn BPMN or to perform business process mapping in your commercial project, you will find Visual Paradigm useful.
Try NowBPMN, short for Business Process Modeling Notation, is widely used modeling language for creating process workflows or business process flowcharts. BPMN introduces a set of graphical notations that can be easily understood by everyone, from technical people such as business analysts, software developers, and data architects to business stakeholders such as the end users and other business stakeholders. This helps people communicate process workflow design ideas effectively.

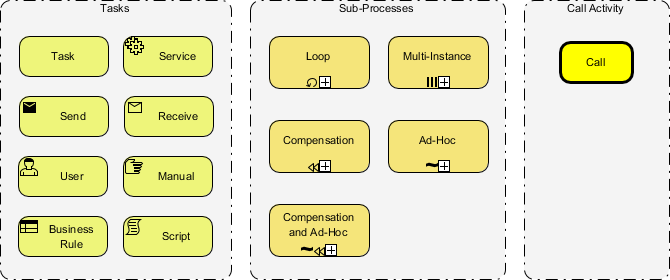
A BPMN Activity is simply "Work" that a company or organization performs in a business process. An Activity is can be atomic (Tasks) or decomposable (Sub-Processes). There are basically three BPMN activity types:
For BPMN Task, the nature of task can be further specified by applying a ‘task type’.
In this article, we will go cover each of these BPMN activity types in detail.
A BPMN task is an atomic activity within a process flow. You create a task when the activity cannot be broken down to a finer level of detail. Generally, a person or applications will perform the task when it is executed.
In BPMN 2.0, there are different types of tasks identified for use in representing more specific behavior that tasks might represent. Here is a list of BPMN 2.0 task type:

In the following sections we will go over each of these BPMN task types by providing you with an example for each of them.
A Service Task is a Task that uses a Web service, an automated application, or other kinds of service in completing the task.

The example below shows the process of answering a question in a forum. A Service Task is used to represent the publishing of answer on Twitter, through the web service they provided.

A Send Task is represents a task that sends a Message to another pool. The Task is completed once the Message has been sent.

The example below shows the process of article approval, a Send Task is used to represent the creation and delivery of rejection message from moderator to author.

A Receive Task indicates that the process has to wait for a message to arrive in order to continue. The Task is completed once the message has received.

The example below shows the use of Receive Task in courier pickup management. The task Receive Pickup Request is activated only when the message is received. In this case, it’s the pickup request.

A User Task represents that a human performer performs the Task with the use of a software application.

The example below shows the process of handling an order. User Task is used to represents the order approval task, which is done by the buyer (i.e. human performer) through interacting with the shopping system (i.e. software application).

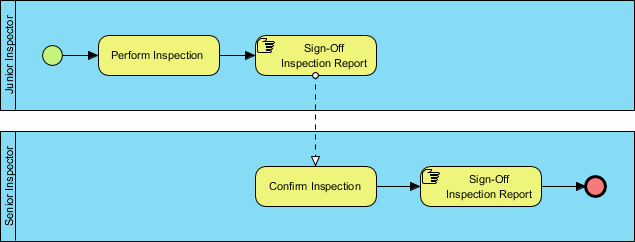
A Manual Task is a Task that is performed without the aid of any business process execution engine or any application.

The example below shows the process of Cart Inspection. The tasks about sign-off are both manual task that are performed without the aid of any process execution engine or software systems.
Business Rule Task is newly added in BPMN 2.0. It provides a mechanism for a process to provide input to a Business Rules Engine and then obtain the output provided by the Business Rules Engine.

The example below shows the use of Business Rule task in analyzing the result of surveys. It is expected that a business rule engine will be used in analyzing the data collected from the survey, and producing the result of analysis in return.

A Script Task is executed by a business process engine. The task defines a script that the engine can interpret. When the task begin, the engine will execute the script. The Task will be completed when the script is completed.

The example below shows the process loan request approval. A Script Task Check Credit is used in reviewing the credit status of applicant, which is done by executing a pre-written script.

In BPMN, a sub-process is a compound activity that represents a collection of other tasks and sub-processes. Generally, we create BPMN diagrams to communicate processes with others. To facilitate effective communications, we really do not want to make a business process diagram too complex. By using sub-processes, you can split a complex process into multiple levels, which allows you to focus on a particular area in a single process diagram.

BPMN specifies five types of markers for Sub-Processes. We will go cover each of them in the sections below.

A Sub-Process with loop marker indicates that the sub-process repeats itself in sequence.

A Sub-Process with Multi-Instance marker indicates that the sub-process can run with other identical sub-processes simultaneously.
A Sub-Process with Compensation marker, or simply called a compensation sub-process, represents a collection of tasks that describe some part of the compensation method.

A Sub-Process with Ad-Hoc marker represents a collection of tasks that exist solely for handling a specific case.

A BPMN Call Activity references an Activity defined in a process that is external to the current process definition. It allows you to create a reusable process definition that can be reused in multiple other process definitions.
The figure below shows a BPMN Call Activity example. It consists of a Call Activity Register that references the Register task defined in a global process.

Want a reliable BPMN tool that helps you in learning how to draw BPMN diagram? Try out Visual Paradigm. It features an intuitive BPMN editor that allows you to create BPMN easily with drag-and-drop. You can create BPMN diagrams in no time.
Try it Free