Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. BPMN was developed by the Business Process Management Initiative in 2000. The aim was to standardize how processes were visually represented, and that aim has been carried on since 2004 by Object Management Group (OMG).
The objective of BPMN is to support business process management for both technical users and business users by providing a notation that is intuitive to business users yet able to represent complex process semantics.
A key element of BPMN is the choice of shapes and icons used for the graphical elements identified in this specification. The intent is to create a standard visual language that all process modelers will recognize and understand. The basic shapes of BPMN are very similar to flow diagrams, but instead of representing pure logical stages, they can also represent business-specific actions, like messaging other departments, and escalating issues.
| Element | Symbol | Description |
| Activity | An activity is a work that is performed within a business process. | |
| Event | An event is something that happens during the course of a process. | |
| Gateway | A gateway is used to control the divergence, and convergence of sequence flows in a process. | |
| Flow | Two major flow elements are core to BPM:· A sequence flow is used to show the order that activities will be performed in a process.· A message flow is used to show the flow of messages between two participants of a process. |
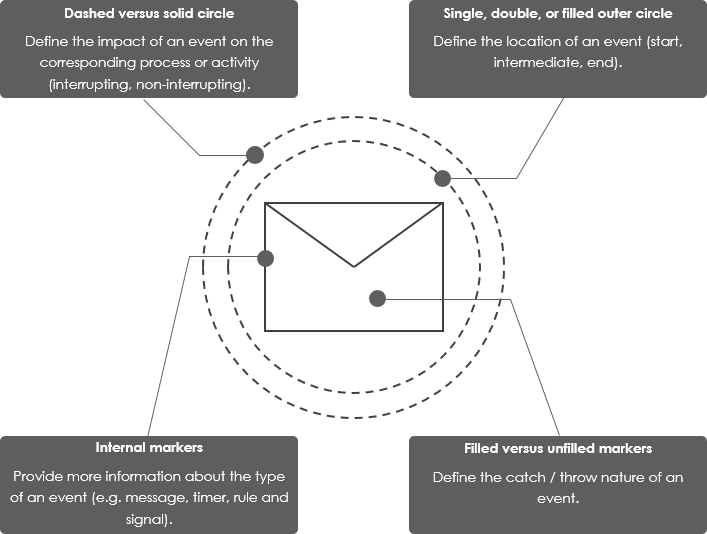
An event is a common Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) process modeling element that represents something that “happens” during the course of a process. In BPMN, events are expressed as circles. Events indicate when some event occurs at the start, end or during a process (as opposed to when some task or activity is performed):
![]()
Simple BPMN Diagram Example
![]()
A boundary event is an event shown on an activity boundary that can be triggered or thrown at any time while the associated task or activity is being performed. In other words, a boundary event is a type of intermediate event.
In the example below, a Timer boundary event is shown. Some boundary events are time-based while others are based on a condition which must resolve to ‘True’ in order for that branch of the flow to proceed.
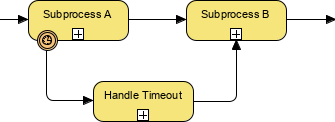
Introduced in BPMN 2.0 is the concept of non-interrupting events. Interupting and non-interupting events are only relevant to intermediate events, especially boundary intermediate events. Boundary events can further be divided into two types: interrupting and non-interrupting, as a boundary events are associated with flow elements and can be configured to interrupt their usual behavior. They are illustrated with a solid line and a dashed line respectively.
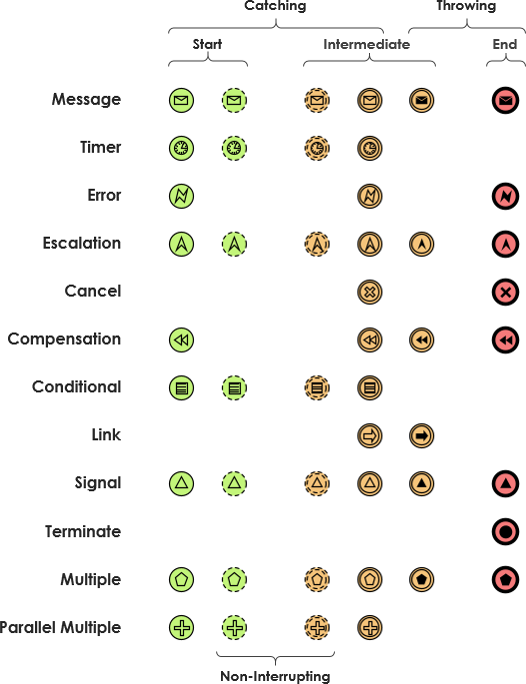
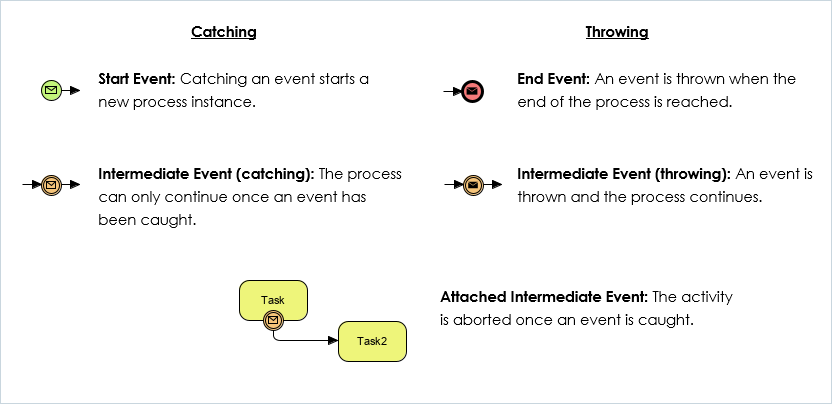
In BPMN there are three types of events. Start Events, Intermediate Events, and End Events. All of these can be catching and throwing events.
Many different types of events can appear in a business process, and BPMN is capable of supporting most of them. In total, BPMN 2.0 supports more than 60 different types of events.