Gateways determine what path is taken through a process that controls the flow of both diverging and converging Sequence Flows. That is, a single Gateway could have multiple inputs and multiple output flows. The term “gateway” implies that there is a gating mechanism that either allows or disallows passage through the Gateway–that is, as tokens arrive at a Gateway, they can be merged on input and/or split apart on output as the Gateway mechanisms are invoked. If the flow does not need to be controlled, then a Gateway is not needed.
Gateways, like Activities, are capable of consuming or generating additional control tokens, effectively controlling the execution semantics of a given Process. The main difference is that Gateways do not represent ‘work’ being done and they are considered to have zero effect on the operational measures of the Process being executed (cost, time, etc.).
All Gateways are represented with a diamond shape, with different icons within to distinguish the type of Gateway. In BPMN we can divide Gateways element into the following categories:
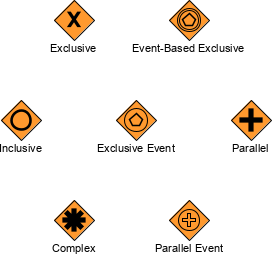
![]()
A diverging Exclusive Gateway (or XOR Gateway) is used to create alternative paths within a Process flow. For a given instance of the Process, only one of the paths can be taken.
When the execution of a workflow arrives at this gateway, all outgoing sequence flows are evaluated in the order in which they are defined. The sequence flow whose condition evaluates to true is selected for propagating the token flow.
Note that the semantics of an outgoing sequence flow:
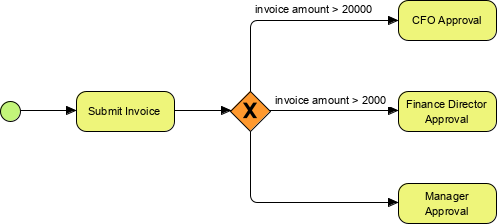
The following diagram shows an exclusive gateway that will choose one sequence flow based on the value of a property, in this example, the invoice amount. Only two flows have conditions on them going to CFO Approval and Finance Director Approval. The last sequence flow has no condition and will be selected by default if the other conditional flows evaluate to false.
The event-based gateway also can be used to instantiate a process. When this is the case the Event-Based Exclusive Gateway icon has only a single circle within the diamond. When used to start a process, the Event-Based Exclusive Gateway allows the process to start in several ways based on the event that triggers it.
![]()
Parallel gateways are used to represent two tasks in a business flow. A parallel gateway is used to visualize the concurrent execution of activities. A parallel gateway models a fork into multiple paths of execution, or a join of multiple incoming paths of execution.
A parallel gateway can have both fork and join behavior if there are multiple incoming and outgoing sequence flows for the same parallel gateway. In this case, the gateway will first join all the incoming sequence flows, before splitting into multiple concurrent paths of execution.
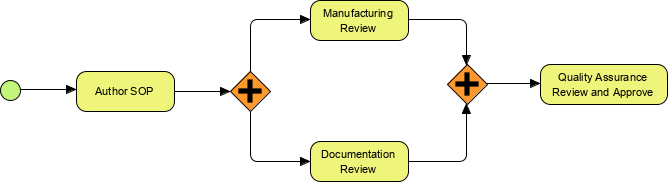
The following diagram shows a definition with two parallel gateways.
![]()
An inclusive Gateway specifies that one or more of the available paths will be taken. They could all be taken, or only one of them.
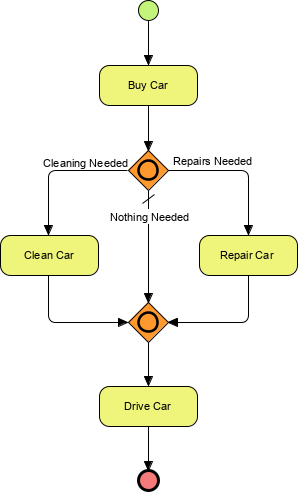
The first OR gateway represents the control of the flow of the process along one or more paths in the model.
The second OR gateway represents the reconnection of those paths and the continuation of flow.

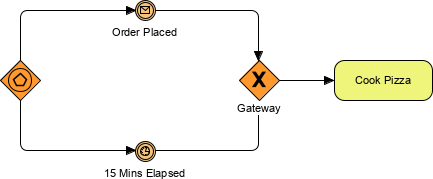
An exclusive event-based gateway is used to branch a process when alternative paths are determined by events (various messages or signals) rather than by conditional flows. This can happen when the decision about one of the alternative paths is taken by someone out of the process.
A signing contract process expects a signal regarding a client’s decision during the negotiation process. Further development of the process depends on this decision.
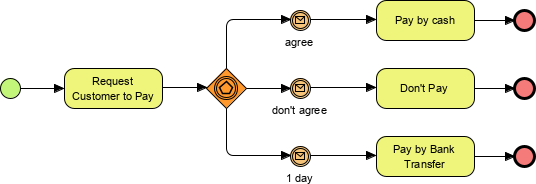
An exclusive event-based gateway, the decision is made based on whichever the associated intermediate event occurs first.
A complex decision gateway allows for a more expressive decision within a business process. Multiple factors, rules, and analyses can all combine to yield results. The analysis should result in at least one path always being taken.
![]()
A student takes an SAT examination. If the student scores under an 800 (the possible scores range from 200 to 1600), the student will enroll in an expensive class to improve his test score – and then retake the exam. If the student performs moderately, he will read a low-cost book designed to help him improve his score – and then retake the exam. If the student scores above 1000, he will immediately attend university.
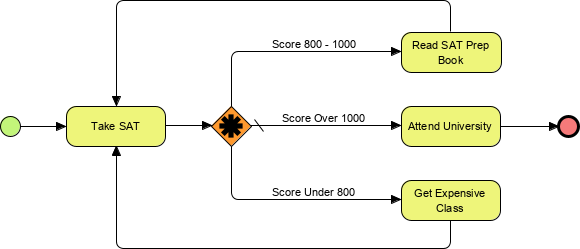

A Parallel Event-Based gateway is similar to a parallel gateway. It allows for more than one process to happen at the same time. It is important to note that while the Event-Based Parallel Gateway will allow multiple events to pass through and start the corresponding portion of the process, it does not wait for all of the events to arrive. That is, it does not wait and synchronize the events before the start of each processing path is permitted.
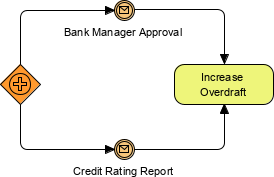
Event Gateways can be used to instantiate a Process. By default the Gateway’s instantiate attribute is false, but if set to true, then the Process is instantiated when the first Event of the Gateway’s configuration is triggered. In this example, if your Bank Manager Approval event is triggered then the Increase Overdraft process will be executed.
We now know how to use the seven different types of gateways in BPMN modeling. Gateways can define all the types of Business Process Sequence Flow behavior: