Business process modeling is a means of representing the business activities, the information flow and decision logic in business processes. It externalizes the business knowledge with a view to agree and bind all stakeholders in a representation that is shared within an organization and is reflected in its information systems. With the power of visualization, business process modeling is used to:
Business Process Management is “old school”, while Business Modeling and Analysis are more trendy new stuff? With all terminology and current trends, it is easy to get confused. So what is the difference between them?
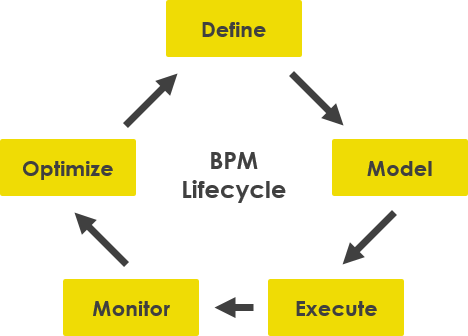
A BPM methodology follows a particular “lifecycle” of phases wherein each phase, a specific set of activities are performed. Simply put, these are the things you will do and the order in which you will do them to continuously improve and control your processes. The standard or common BPM methodology follows these life-cycle phases: Design, Model, Execute, Monitor and Optimize (DMEMO).
Business process modeling is the analytical representation or illustration of an organization’s business processes which is widely viewed as a critical component in successful business process improvement. It is used to map out an organization’s current processes (as-is model) to create a baseline for process improvements and to design future processes (“to-be” model) with those improvements incorporated.
Process modeling often uses Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN), a standard method of illustrating processes with flowchart-like diagrams that can be easily understood by both IT and business managers.
One effective technique for transforming vision into results is to develop and populate an As-Is and To-Be BPMN diagrams. The As-Is diagram describes the present state of the organization’s process, culture, and capabilities. The To-Be diagram describes the future state; in other words, how the organization’s process, culture, and capabilities will appear in the future. This studying of As-is and To-be process results in identifying the difference between the current and target business state, known as a gap, which is an important part of any business process reengineering/improvement initiative.
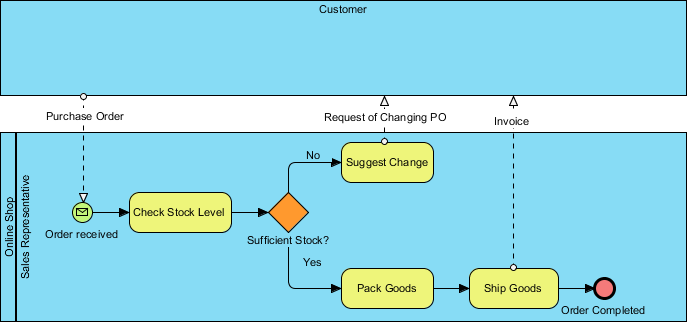
In the online shop example below, the process begins with the sales representative receives a purchase order from a customer and proceeds to check the stock level. If there is enough stock on hand to meet with the order, the sales representative will pack them. The process ends with shipping them along with an invoice. In case of insufficient stock, the sales representative will suggest the customer amend the purchase order.
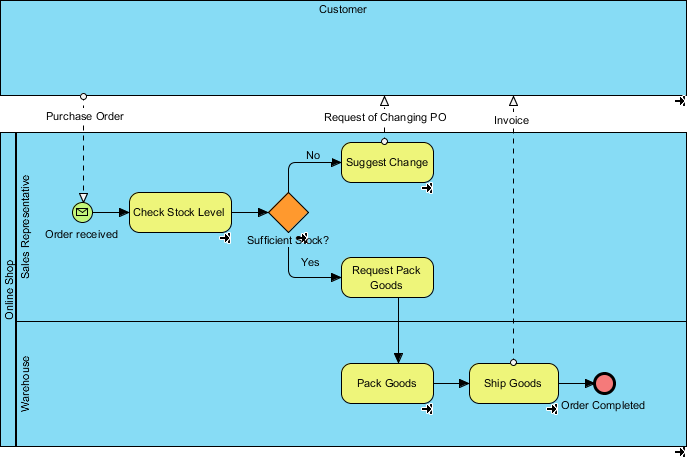
Once the business process of your existing operation has been created, you can then derive the to-be process model by considering and projecting the necessary improvements or changes needed to be made based on the existing to-be process. Walkthrough the steps in this tutorial to see how things work.
Re-design to Enhance the Current Process in To-be Process
Let’s just say that our business has grown so much that we now have a warehouse to keep our stocks. So we are looking for ways to improve our current (as-is) process to better allocate the new resources. Furthermore, we will show an example of modeling the enhancement below in a to-be process diagram.
Visual Paradigm is a modeling software. It supports various modeling standards including UML, SysML, SoaML and, BPMN.
Listed below are some of the key BPMN editor features:
Create new shapes quickly and accurately through drag-and-drop.
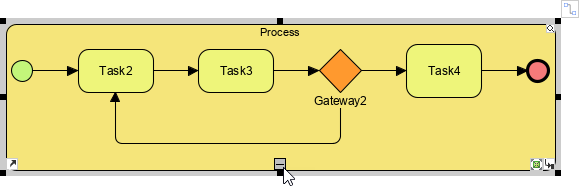
Expand and collapse sub-process shapes to show or hide its internal process content.
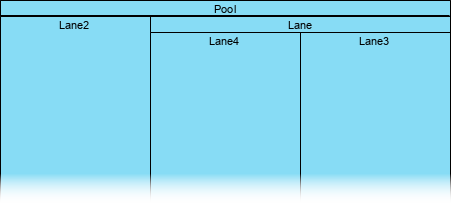
Create multiple levels of pools and lanes to reflect the actual organizational structure.
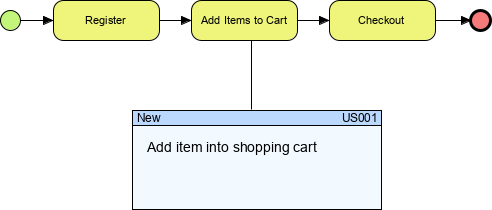
Discover and record requirements from the business process model by creating and integrating user stories with tasks and sub-processes.
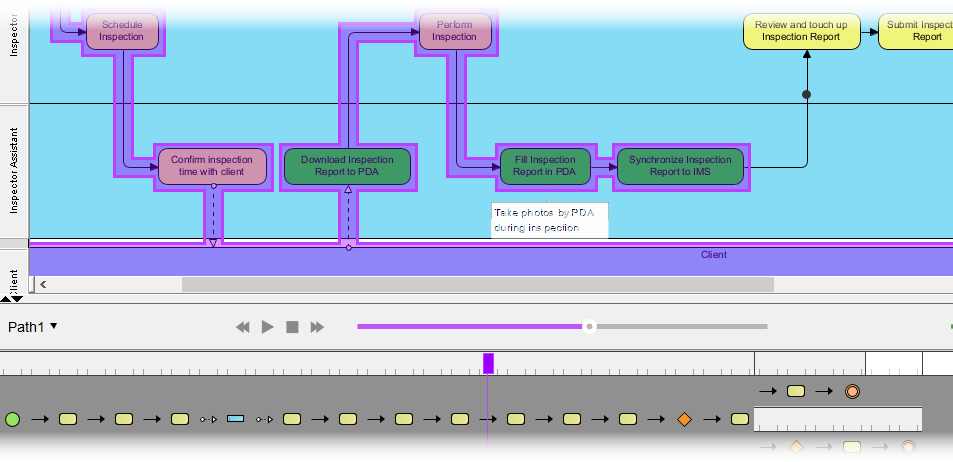
Visually simulate the execution of the business process for studying resource consumption (e.g. human resources, devices, etc.) throughout a process.
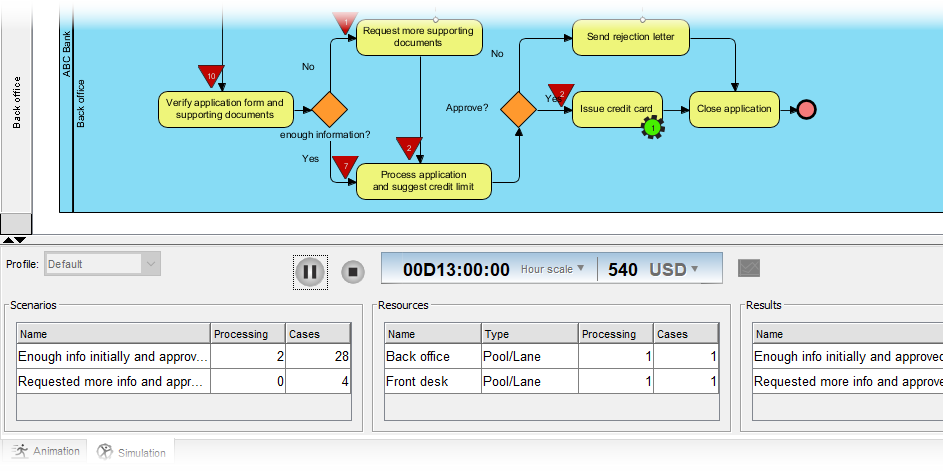
Clears barrier encountered in studying an animated process flow with static images.