Project scope management is the primary knowledge area out of ten knowledge areas in PMBOK which includes the processes required to ensure that the project includes all the work required, and only the work required, to complete the project successfully. A project scope management can help you to understand what the client or the customer is looking for as deliverable, in other words, It is primarily concerned with defining and controlling what is or is not included in the project.
The Figure below provides an overview of the major project scope management processes:
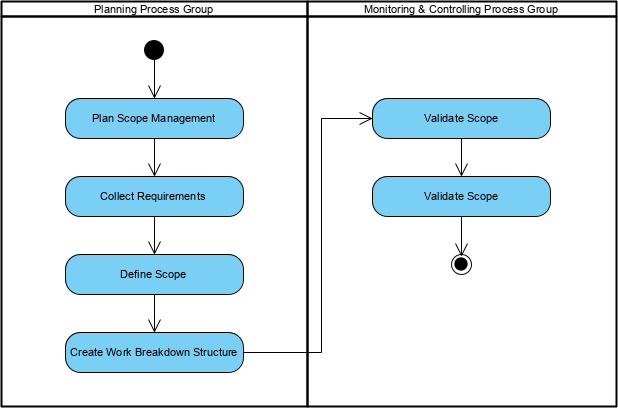
By relating the six process of project scope management knowledge areas against the Process Groups, the project scope management has major role only in two process groups:
| Project Management Process Groups | |||||
| Knowledge Areas | Initiating Process | Planning Process Group | Executing Process Group | Monitoring and Controlling Process Group | Closing Process Group |
| 5. Project Scope Management | 5.1 Plan Scope Management
5.2 Collect Requirements 5.3 Define Scope 5.4 Create WBS |
5.5 Validate Scope
5.6 Control Scope |
|||
In the initial stage of a project, Scope will be or might be limited, as work progress goes, Project scope management helps to maintain and balance the scope baselines.
Project scope management is the second knowledge area in PMBOK. As a project manager, you must understand the importance of project scope that helps you ensure all of the required work (and only the required work!) is included in the project. As mentioned above, Project Scope Management has six processes in PMBOK, each of these processes associated with a set of inputs, tools & techniques and outputs as shown in the Figure below:

Each of those 47 processes described in greater detail inside PMBOK® is represented in an Inputs – Tools & Techniques – Outputs diagram like the one below emphasizing that each process consumes input artifacts and produces output artifacts.
Take the first process in the Scope Management knowledge area as an example, “process 5.1 Plan Scope Management” which is the process of creating a scope management plan that documents how the project scope will be defined, validated, and controlled. The key benefit of this process is that it provides guidance and direction on how scope will be managed throughout the project. The inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs of this process are depicted in the mind map as shown in the following.
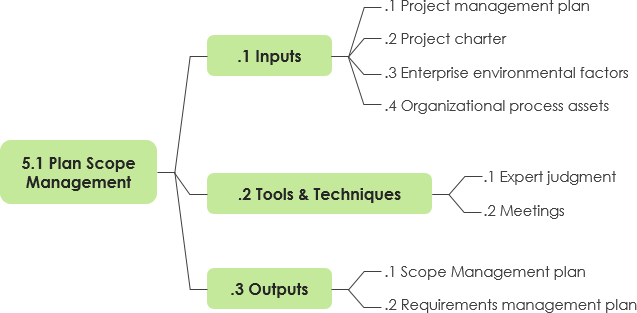
As shown in the mindmap above, the project planning team can produce two main output namely, the Scope Management Plan and the Requirements Management Plan, based on the input documentation developed previously and applying the tools and techniques of consulting with knowledgeable experts (expert judgment) and the team (in the meetings).