A sprint planning meeting is conducted before the start of a sprint. The purpose of this meeting is to determine the sprint plan and set a sprint goal.
Sprint planning includes agreeing on the number of backlog items in the sprint that is the responsibility of the development team and as well as to define the goal for the current sprint and sprint backlog.
During the sprint planning meeting, the product owner describes the highest priority features to the entire team. They will then discuss which stories the team will do in that sprint. The meeting should be attended by the whole team. If additional expertise on specific backlog items are required, then stakeholders can be also invited. The team may include the refinement sessions as well.

Below are some of the benefits of running a successful Sprint Planning meeting:
Best Scrum Software Every Project Needs
A powerful scrum software that supports scrum project management. It features scrum tools like user story map, product backlog management, sprint backlog management, task management, daily scrum meeting, sprint planning tool, sprint review tool, sprint retrospective tool, burndown, impediment, stakeholder and team management.
Each sprint begins with a sprint planning meeting. Typically, for a four-week sprint this meeting should last eight hours. For a two-week sprint, plan for about four hours. As a general rule of thumb, multiply the number of weeks in your sprint by two hours to get your total sprint planning meeting length. The following table illustrates the rule.
| Total Sprint Duration | Sprint Planning Duration |
|---|---|
| 1 week | 2 hours |
| 2 week | 4 hours |
| 3 week | 6 hours |
| 4 week | 8 hours |
Now, let’s review what we need to prepare for each of the scrum roles before we attend the Sprint Planning Meeting:
This meeting is split into two sessions. In the first session, the product owner reviews the list of features and defines what needs to be built during the next sprint. The next session involves identification of tasks that need to be executed, in order to complete the build. The sprint planning meeting should yield the sprint goal and the sprint backlog.
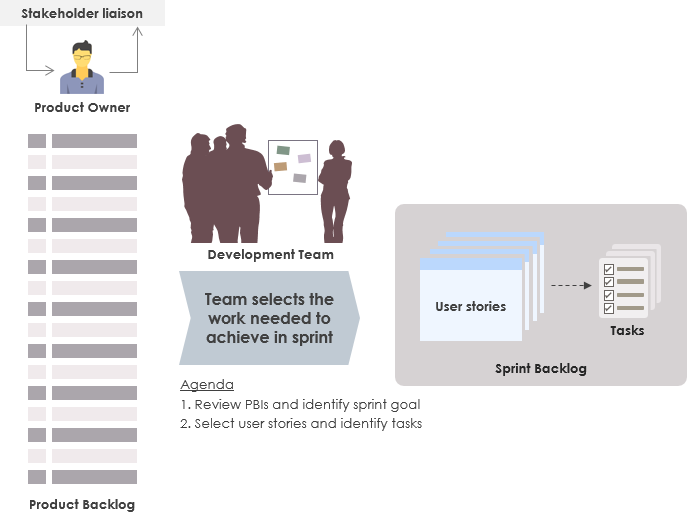
Part one of the sprint planning meeting is a review of the product backlog items the Product Owner will ask the team to forecast and deliver. This is the time for the product owner to describe what she wants to make available by the end of the next sprint. During this part of the meeting, it is not uncommon for the team to banter back and forth with the product owner, asking clarifying questions and driving away ambiguity. By the end of sprint planning part one, the team will select a sprint goal: a one-sentence description of the overall outcome of the sprint. This helps later when questions about depth and breadth come up: if the work does not directly tie to the sprint goal, then it is not done during the sprint. The key activities to be conducted in Part I of the Sprint Planning Meeting are:
During part two of the sprint planning meeting, the team decides how the work will be built. In this meeting the team will begin decomposing the product backlog items into work tasks and estimating these in hours. The product owner must be available during this meeting but does not have to be in the room. In fact, many teams find it helpful to work without product owner during this detailed part of the meeting. Knowing that the product owner is available yet not having her observing all of the discussion about the best way to implement a feature can be freeing for many teams. Many teams find they enjoy discussing many implementation possibilities without worrying that the product owner will panic or misunderstand. If the product owner does remain in the room, the Scrum Master needs to take charge of this part of the meeting, keeping the team focused and free to explore possibilities without being limited by the product owner’s own ideas or opinions. The key activities of the Part II of Sprint Planning are:
| About Visual Paradigm |
 Visual Paradigm help organizations stay competitive and responsive to change faster and better in today’s fast changing environment. Our award-winning products are trusted by over 320,000 users in companies ranging from small business, consultants, to blue chip organizations, universities and government units across the globe. It enables organizations to improve business and IT agility and foster innovation through popular open standards and process frameworks.Visual Paradigm, a killer Agile feature in 2018, introduced Scrum Process Canvas for automating the way a Scrum team to create, manage and deploy software application that empowers the team to continuously improve their performance at unprecedented speed and scale. Visual Paradigm help organizations stay competitive and responsive to change faster and better in today’s fast changing environment. Our award-winning products are trusted by over 320,000 users in companies ranging from small business, consultants, to blue chip organizations, universities and government units across the globe. It enables organizations to improve business and IT agility and foster innovation through popular open standards and process frameworks.Visual Paradigm, a killer Agile feature in 2018, introduced Scrum Process Canvas for automating the way a Scrum team to create, manage and deploy software application that empowers the team to continuously improve their performance at unprecedented speed and scale.
Manage the Entire Scrum Process in One Page
|