A story point is a metric used in agile project management and development to estimate the difficulty of implementing a given user story, which is an abstract measure of effort required to implement it. In simple terms, a story point is a number that tells the team about the difficulty level of the story. Difficulty could be related to complexities, risks, and efforts involved.
Story point estimation, a kind of relative estimation, is typically performed at the Product Backlog Grooming Sessions and the Product Backlog is evaluated by the team who responsible for the actual development and testing work.
In order to make the Sprint Planning more efficient in practice, PO and the Team will make a rough estimation called product backlog grooming before the Sprint Planning and check for:
Best Scrum Software Every Project Needs
A powerful scrum software that supports scrum project management. It features scrum tools like user story map, product backlog management, sprint backlog management, task management, daily scrum meeting, sprint planning tool, sprint review tool, sprint retrospective tool, burndown, impediment, stakeholder and team management.
When the development team conducts an estimation, it is recommended to abandon the traditional “human-day” assessment method, using the point of the story point, using the Fibonacci number (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21…) to estimate the story point (see Planning Poker article for detail).
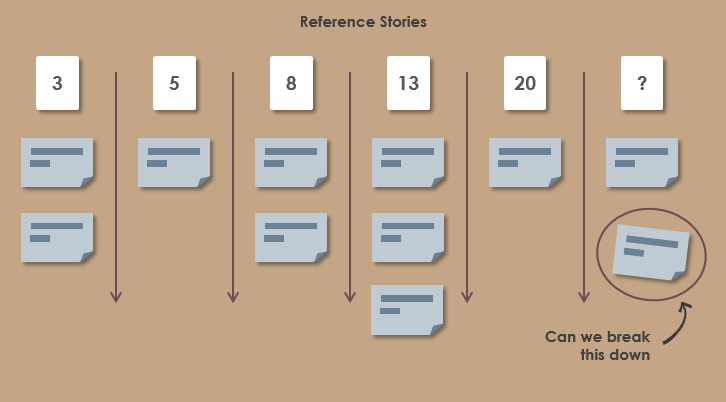
In order to do that each team would have to find a baseline story. It does not necessarily to be the smallest one, but the one that everyone within the team can resonate with. Once determined, sizing of all the user stories should be initiated by comparing them against the baseline.
When estimating new stories all you have to do is pick a story and say: “will this take longer than reference story x?” or “will it be less than reference y?” With enough reference stories there should be a suitable comparator to find a similar sized story and give it the same points or a bit more or a bit less based on a considered factor.
While estimating story points, we assign a point value to each story. Relative values are more important than the raw values. A story that is assigned 2 story points should be twice as much as a story that is assigned 1 story point. It should also be two-thirds of a story that is estimated 3 story points.
In addition, it is important to note that when the single story point of the assessment is greater than 21, the user story needs to be split again, and the single user story point is no more than 8 is the most rational state.
| About Visual Paradigm |
 Visual Paradigm help organizations stay competitive and responsive to change faster and better in today’s fast changing environment. Our award-winning products are trusted by over 320,000 users in companies ranging from small business, consultants, to blue chip organizations, universities and government units across the globe. It enables organizations to improve business and IT agility and foster innovation through popular open standards and process frameworks.Visual Paradigm, a killer Agile feature in 2018, introduced Scrum Process Canvas for automating the way a Scrum team to create, manage and deploy software application that empowers the team to continuously improve their performance at unprecedented speed and scale. Visual Paradigm help organizations stay competitive and responsive to change faster and better in today’s fast changing environment. Our award-winning products are trusted by over 320,000 users in companies ranging from small business, consultants, to blue chip organizations, universities and government units across the globe. It enables organizations to improve business and IT agility and foster innovation through popular open standards and process frameworks.Visual Paradigm, a killer Agile feature in 2018, introduced Scrum Process Canvas for automating the way a Scrum team to create, manage and deploy software application that empowers the team to continuously improve their performance at unprecedented speed and scale.
Manage the Entire Scrum Process in One Page
|