Comparing logical and physical ERD
Entity relationship diagram (ERD) represents a detailed picture of the entities needed for a business. In forward engineering, ERD will be transformed into a relational database eventually. There are at least two types of ERD – Logical and Physical. They are used in different stages of development and are inter-related.
Logical ERD models information gathered from business requirements. Entities and relationships modeled in such ERD are defined around the business's need. The need of satisfying the database design is not considered yet.
Physical ERD represents the actual design of database. It deals with conversion from logical design into a schema level design that will be transformed into relational database. When modeling a physical ERD, Logical ERD is treated as base, refinement occurs by defining primary keys, foreign keys and constraints. Sometimes, relationships need to be resolved by introducing additional tables, like a Linked table for a many to many relationship.
Since physical ERD and logical ERD represent the business requirement and database schema respectively, comparing physical and logical ERD helps to find out the differences between them in order to confirm the database is exactly following the initial business requirements regardless of the changes.
Two ERDs are compared: one for modeling the Logical Model and another one for modeling the Physical Model. With the features of Visual Diff, the differences between Logical and Physical ERD can be found easily.
- In Logical ERD diagram, select Modeling > Visual Diff from the toolbar.
The overview of Visual Diff window:NOTE: Alternatively, you can right click on diagram background and select Utilities > Visual Diff... from the pop-up menu.
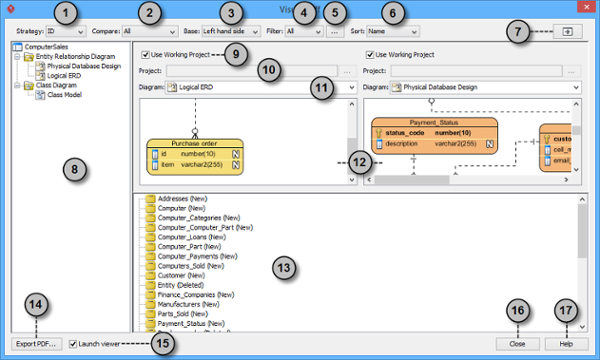
The Visual Diff window No. Name Description 1 Strategy It determines how two diagrams will be compared. Select the appropriate strategy that suits your application most.
ID: Shapes will be matched base on their internal ID. Differences between shapes that have same ID will be displayed in the result pane. This strategy is usually used to visualize the changes of same shapes in two projects.
Name: Shapes will be matched base on their names. This strategy is useful when visualizing differences for external works. One of typical examples is to compare databases and class models.
Transitor: Shapes will be matched base on their transition established by Model Transitor. This way of comparison is usually used to visualize the differences between model elements.2 Compare It determines how two diagrams will be displayed for comparison.
All: Both view and model elements are displayed.
View: Differences, such as coordinates, width, height and color of shapes, are displayed.
Model Element: Differences, such as model name, are displayed.3 Base It determines which diagram is used as a base for comparison.
Left hand side: Comparison is based on the diagram on the right hand side. For example, if there is a shape absent on the left hand side, but appear on the right hand side, the shape is said to be a new shape.
Right hand side: Comparison is based on the diagram on the right hand side. For example, if there is a shape absent on the left hand side, but appear on the right hand side, the shape is said to be a removed shape.4 Filter It determines what kind of comparing data will be displayed on the result pane.
All: Display all kinds of differences including the addition, modification and removal of shapes.
New: Display only results about the addition of shape and then hide the rest.
Modified: Display only results about the modification of shapes and then hide the rest.
Deleted: Display only results about the removal of shapes and then hide the rest.5 Filter Model Type... It determines what type of model elements will be shown on the result pane. When Filter Model Type window pops out, uncheck the type of model elements you don't want to be shown; otherwise, check the type of model elements you want it to be shown. 6 Sort It determines how the result of comparison be displayed on Result pane. You can select sort by Type, by Name or by Change Type.
Name: All model elements are sorted by their name.
Change Type: All model elements are changed their type.
Type: All model elements are sorted by their type.7 Maximum Press this button to enlarge the Visual Diff window to the maximum screen size. Press it again to reduce the window to the default size. 8 Diagram list It lists all diagrams on projects selected in the left hand side and the right hand side respectively. 9 Use Working Project Check it if you want to select a diagram for comparison within the current working project. 10 Project Select and open a project directory for comparison. 11 Diagram Select and open a specific diagram for comparison after selecting a project. 12 Display pane A pane that has two sides. Each side displays a diagram out of a project. 13 Result pane The differences of the two projects are shown here. When the word New is shown behind a task that means it is newly added, the word Deleted is shown behind a task that means it is deleted. 14 Export PDF... Click it to save a document of the two compared diagrams in your computer as PDF. 15 Launch viewer Open the exported file after you have export a PDF file. Check it to open the PDF file. If you uncheck it, nothing will happen even after you have exported a PDF file. 16 Compare Click it to start comparing two diagrams. 17 Close Close Visual Diff window. Description of various parts of Visual Diff window - In Visual Diff window, the left hand side window shows the currently opened diagram by default. You may remain it unchanged; otherwise uncheck Use Working Project on the left hand side if you want to select a diagram in other projects to compare with. Click ... button in Project to select the directory of other projects. Similarly, check/ uncheck Use Working Project on the right hand side window.
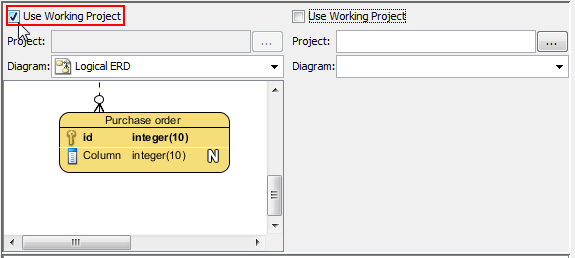
Select Use Working Project - Select the Physical ERD to compare with from the drop-down menu of Diagram.
The two diagrams are shown side by side on display pane. However, the ways of comparison has not yet been configured. Let's configure them one by one in the following steps.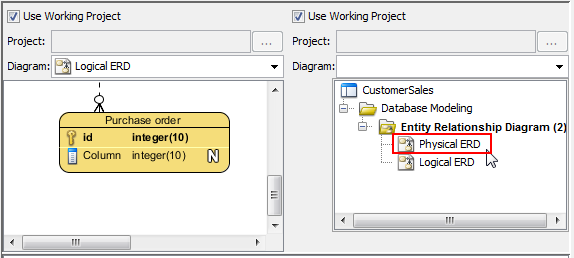
Select a diagram 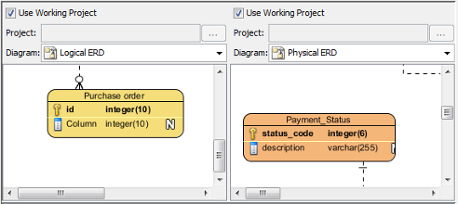
Two diagrams are selected - At the top of the Visual Diff window, adjust the Strategy, Compare, Base and Filter.
- Once everything is set, the differences of the two diagrams will be shown on the result pane.
- If you want to view a specific shape, you may click its node on the result pane and then the selected shape will be painted in dark purple on the display pane.
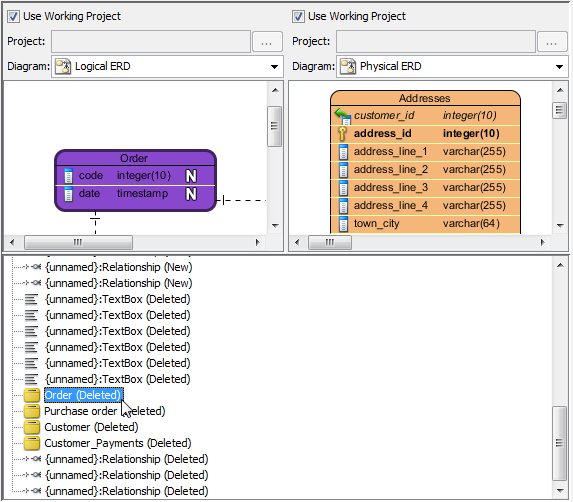
Select a node in the result pane
Related Resources
The following resources may help you to learn more about the topic discussed in this page.
| 2. Comparing as-is and to-be business process diagram | Table of Contents | Chapter 4. Using design pattern |
