Using Partial Table
In a one-to-one identifying relationship, an entity may be a subordinate of the related entity; that is, the subordinate entity has columns which also belong to its superior entity in the real world situation. Visual Paradigm promotes the idea of Split Table with stereotype of Partial which allows developers to optimize the size of database, and minimizes the redundant persistent classes for handling one-to-one identifying relationship. In order to reduce the risk of appending a new column to an existing database table, Split table supports developers to add new columns to the partial table with a one-to-one identifying relationship linked to the existing table. Visual Paradigm allows you to split the entity into two and convert the subordinate entity to be a Partial Table in a one-to-one identifying relationship.
Splitting Table
You can split an entity into two associated entities with a one-to-one identifying relationship. There are two ways you can take to split a table.
Using popup menu
- Right click on an entity.
- Select Split Table from the popup menu.
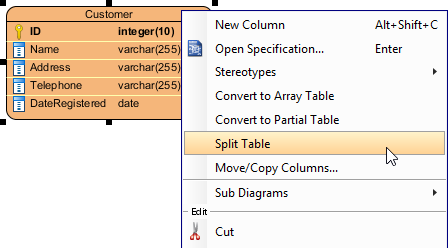
Split table
Using Resource Catalog
- Move the mosue pointer over an entity.
- Press on the Resource Catalog button and drag it out.
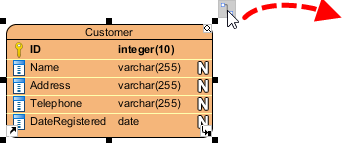
Split table using resource-centric interface - Release the mouse button and select One-to-One Relationship -> Partial Table from Resource Catalog.
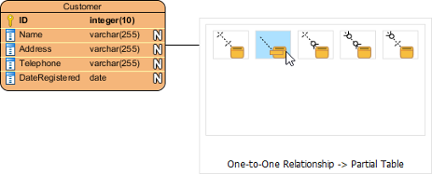
Select One-to-One Relationship -> Partial Table
Both ways will result in popping up the Split Table window. In the window, enter the name of the new entity and select the columns from the list of Original to Partial, and click OK.
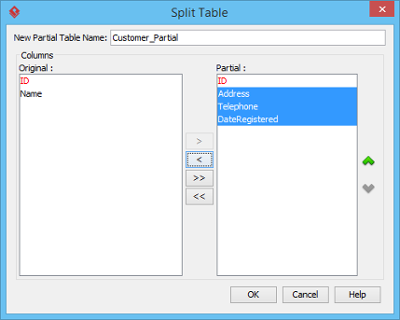 |
| Split Table window |
An entity stereotyped <<Partial>> is created.
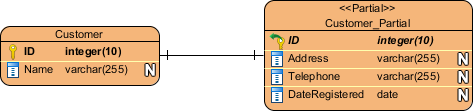 |
| Partial table created |
Converting to a Partial table
You can convert an entity to a Partial Table in a one-to-one identifying relationship.
- Right click on the entity.
- Select Convert to Partial Table from the popup menu.
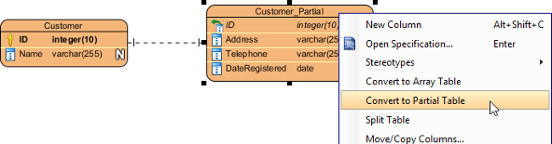
Convert to Partial Table
The entity is stereotyped <<Partial>>.
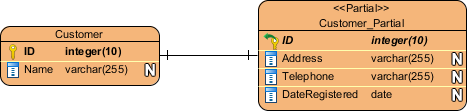
Partial table converted
Related Resources
The following resources may help you to learn more about the topic discussed in this page.
| 15. Using Array Table | Table of Contents | 17. Mapping Object Model to Data Model |
