What is SWOT Analysis?
Companies need to understand the changes in their business environment for them to achieve business goals. SWOT analysis is often used for strategic decision-making by enterprises. In strategic planning, SWOT should be regarded as a commonly used analysis method, Strength – competitive advantage, Weakness – disadvantage, Opportunity, Threat.
Strengths and weaknesses are the internal factors of the company (products), which are affected by factors such as product quality, materials, personnel, machines, channels, and services. Opportunities and threats are the external factors of the company (products) and are affected by the market, economy, society, and policies. The analysis of SWOT guides organizations to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the product. Only by better understanding oneself, understanding the opponent, and understanding the environment can one remain more adaptive and responsive to the changes faster and better.
SWOT Analysis at a glance
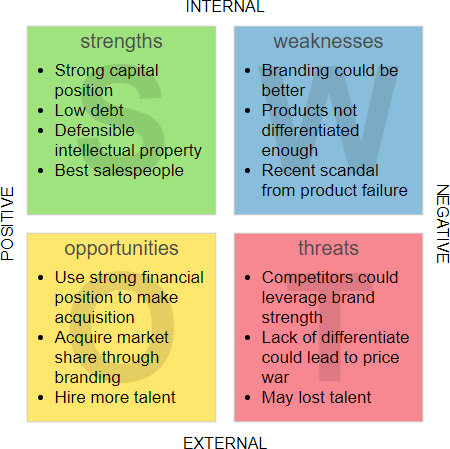
The figure below shows a simple SWOT Analysis example.
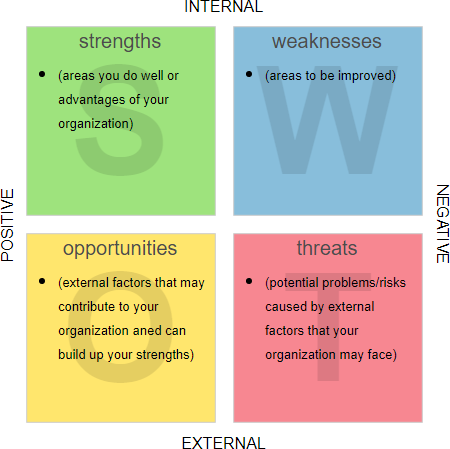
SWOT Analysis – Key Concepts
Internal Factors – Strength and Weakness
- Strength: The ability of a company to surpass its competitors or a company’s unique advantage of improving competitiveness.
- Weakness: An area where an enterprise does not perform well or has failed to do so compared with its competitors, thereby placing itself at a disadvantage compared with its competitors.
The strengths and weaknesses of the product can be analyzed through the following perspectives:
The SW analysis mainly analyzes the comparison between the product’s internal environment and competing products in these possible areas of Quality, Price, Process, Capability, Sales/Services
- Quality
- Product quality safety, stability, reliability, aesthetics, applicability, durability, economy, etc.
- Price
- The same level of product production costs, sales costs, service costs and sales prices (product profitability).
- Process (Production, Efficiency, Delivery)
- Total production volume, production capacity, comprehensive efficiency, per capita output, per capita value-added, and delivery quantity on time.
- Product R&D/production technology (product technology and manufacturing technology)
- New product design and development capabilities, development cycles, patented technologies, proprietary technologies, and technological innovation capabilities.
- Capability
- Talent: Experienced excellent management talents, technical talents, excellent management, technical team, young/passionate.
- Equipment: advanced and efficient production lines, modern high-precision production equipment, inspection equipment.
- Materials: Excellent supplier team, first-rate supply chain, stable supply of high-quality, low-cost materials.
- Method: advanced management methods, management system, unimpeded information (priority of access to information than other adversaries)
- Measurement: advanced measuring instruments, scientific measurement methods, complete quality control system.
- Sales / Service
- Sales: a strong sales network, excellent sales team, rich sales experience and skills, flexible market change response capabilities, excellent brand image, brand value and market recognition, good customer relations, loyal customers.
- Service: perfect after-sales service system, quality service, satisfied customer base.
External Factors – Opportunity, Threat
To adapt to the market and the environment, we must constantly improve ourselves. To adapt to the ever-changing environment and avoid fighting the Red Sea, the products must be upgraded to process iteratively for a company to remain competitive.
- Opportunity: A product has an absolute advantage in a certain area. In this field, the product has a strong competitive opportunity.
- Threat: The unfavorable factors of product development in a certain environment. If you do not take decisive strategic actions, this unfavorable trend will lead to the weakening of the company’s competitive position.
How to perform SWOT Analysis?
- Establish the objective of your SWOT analysis
- Conduct necessary research for your business, industry, and market
- Identify your business’s strengths
- Identify your business’s weaknesses
- Identify potential opportunities for your business
- Identify potential threats to your business
- Develop a strategy and actions to address issues in the SWOT
- Prioritize the order for the actions to be taken as an implementation plan
SWOT Analysis Examples
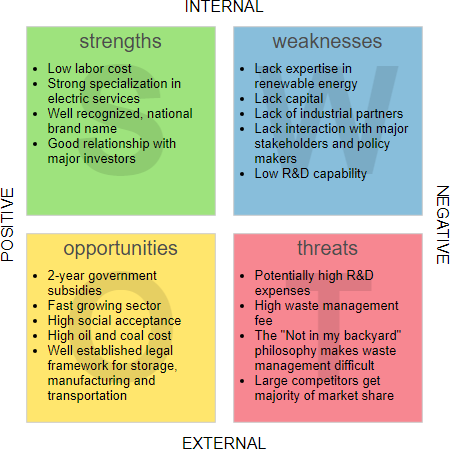
The figure below shows a SWOT Analysis example for the strengths and weaknesses of the renewable energy market.
Performing SWOT Analysis in Visual Paradigm
Let’s see how to perform SWOT Analysis in Visual Paradigm. We will use a simple SWOT Analysis example here. You may expand the example when finished this tutorial.
- Select Diagram > New from the main menu.
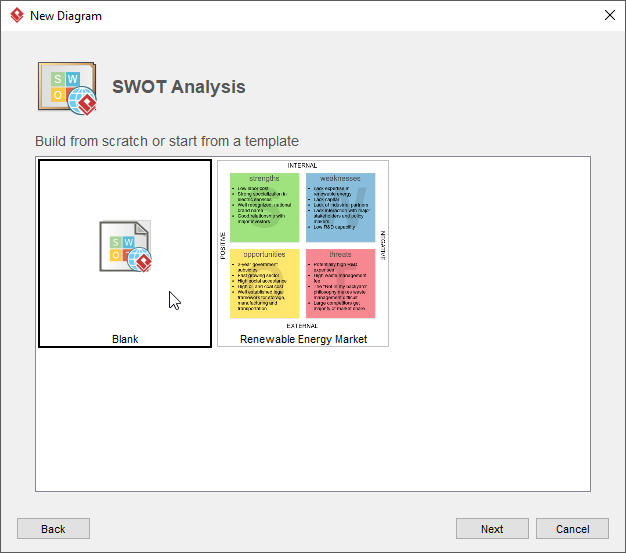
- In the New Diagram window, select SWOT Analysis and click Next.
- You can start from an empty diagram or start from a SWOT Analysis template or SWOT Analysis example provided. Let’s start with a blank diagram. Select Blank and click Next.
- Enter the name of the SWOT Analysis model and click OK.
- Drag the SWOT Analysis shape from the diagram toolbar and drop it onto the diagram.
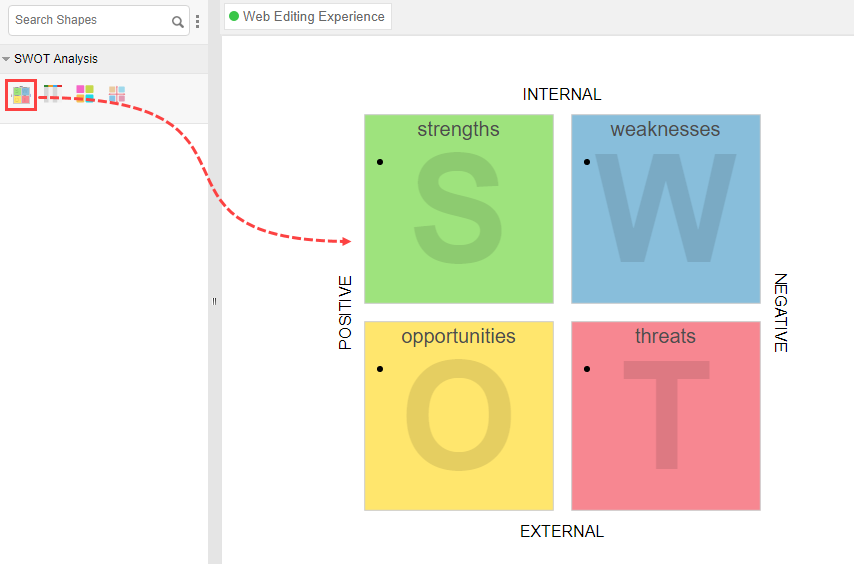
- The editing of a SWOT Analysis model is done via the InfoArt shape. Click on the SWOT Analysis shape to show the InfoArt shape.
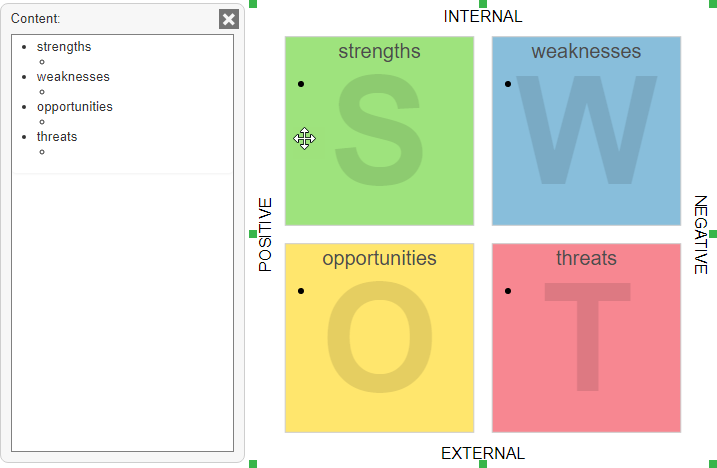
- Start entering the content in InfoArt.
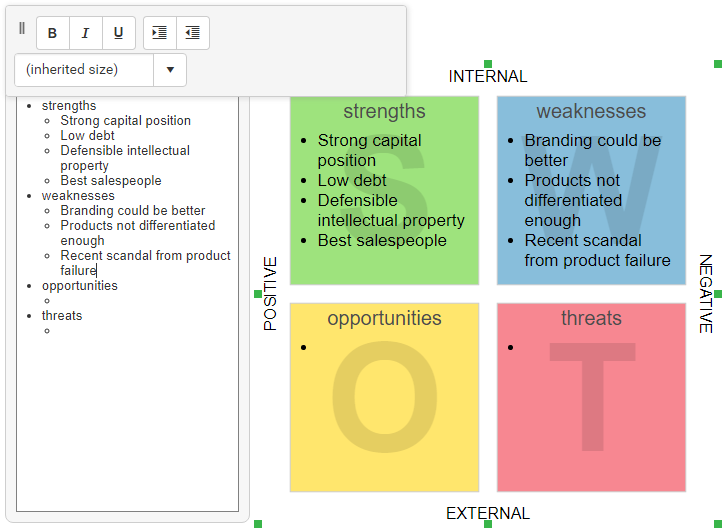
This is the final SWOT Analysis: