Introduction to BPMN Part I
BPMN enables organizations to capture and document their business processes in a clear and consistent manner, ensuring that relevant stakeholders such as process owners and business users are involved in the process. This allows the team to effectively respond to any issues identified in the processes. BPMN provides comprehensive and rich notations that can be easily understood by both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
What is BPMN?
BPMN, which stands for Business Process Model and Notation, is a standardized graphical modeling language used to represent and visualize business processes. It is a widely adopted industry standard for modeling and documenting business processes, as it provides a consistent and easy-to-understand visual representation of a process.
BPMN allows organizations to document their business processes in a way that is easily understood by both technical and non-technical stakeholders. It is a powerful tool for process analysis, design, and optimization. It provides a standard notation for representing the different elements of a process, such as tasks, events, and gateways, as well as the relationships and flows between them.
BPMN models are created using a variety of symbols and shapes that represent different elements of the process. These symbols include start and end events, tasks, gateways, and data objects, among others. Additionally, BPMN provides mechanisms for representing complex process flows, such as branching and merging paths, loops, and parallel processing.
By using BPMN, organizations can create a clear and consistent representation of their business processes that can be easily shared and understood by all stakeholders, from process owners to business analysts, developers, and end-users. This helps to ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same process goals, leading to improved process efficiency, effectiveness, and overall business performance.
Why Use BPMN? The Benefits of Using BPMN
BPMN offers several benefits to organizations, including the ability to define and understand their procedures through Business Process Diagrams. As an industry standard developed by the OMG consortium, a not-for-profit industry group, BPMN provides a standard notation that is readily understandable by all business stakeholders, helping to bridge the communication gap that frequently occurs between business process design and implementation. Moreover, BPMN is simple to learn yet powerful enough to depict the potential complexities of a business process. It is also vendor-neutral with wide tools support, making it a versatile and flexible option for organizations of all sizes and industries. By utilizing BPMN, companies can streamline their processes, reduce inefficiencies, and improve communication and collaboration between teams, resulting in improved overall performance and outcomes.
About this BPMN Guide
The purpose of this guide is to introduce the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). It is divided into four parts and covers the fundamentals of the BPMN notation, including the various graphical objects that make up the notation and how they are used in a Business Process Diagram. Additionally, it provides a step-by-step guide on how to create and draw BPMN diagrams using Visual Paradigm.
Basic Constructs
There are five basic categories of BPMN elements, each representing a unique aspect of a business process.
Swimlanes

Swimlanes are graphical containers that represent participants in a process. Pools and lanes are the two types of swimlanes, and we will discuss them in detail in Part II of this tutorial.
Flow Elements

Flow elements are elements that connect to form business workflows. They are the primary elements that define the behavior of a process. There are three types of flow elements: Events, Activities, and Gateways. We will cover them in Part III of this tutorial.
Connecting Objects

Flow objects are not isolated; they are connected to form a flow. The connectors that link the flow objects are called connecting objects. There are four types of connecting objects: Sequence flows, message flows, associations, and data associations. We will discuss them in Part III of this tutorial.
Data
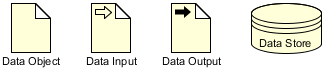
Data is the information that is needed or produced when executing a business process. There are four types of data: Data objects, data inputs, data outputs, and data stores. We will cover these in Part IV of this tutorial.
Artifacts

Artifacts provide additional information about a business process. We will discuss the two types of artifacts, groups and text annotations, in Part IV of this tutorial.